- Formats 48x48, 48x96, 96x96mm
- Universal measuring input
- One binary input
- Up to four switching outputs, one analog output
- Modbus interface
- Two/three-state controller, three-state modulating and continuous controller
- Timer, ramp function
- Programmable user level and function key
- 2 limit value monitoring functions
- Self-optimizationv
- Service counter
- Configuration through keyboard or setup program
CUSTOMIZED INDICATOR CONTROLLER
Customized Indicator Controller
Manufactured at our modern infrastructure, these products are manufactured in tandem with the highest benchmarks of quality. Digital Process Indicator Controller, which are low cost, accurate, rugged and reliable instruments available for indication and single and dual set point On/Off control for general-purpose process control applications.
Compact Controller
To accurately control process temperature without extensive operator involvement, a temperature control system relies upon a controller, which accepts a temperature sensor such as a thermocouple or RTD as input. It compares the actual temperature to the desired control temperature, or set point, and provides an output to a control element. The controller is one part of the entire control system, and the whole system should be analyzed in selecting the proper controller. Compact controllers take less space and are useful for process where you dont require too much processing power.
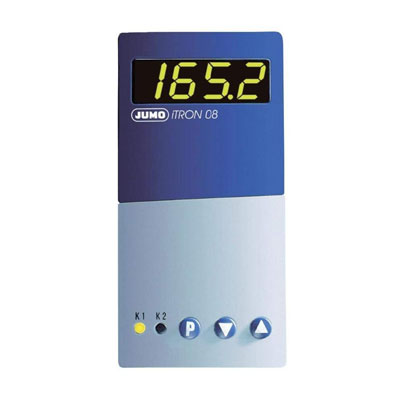

Compact Controller
Control of temperatures, pressures, and other process variables
Two-State Controller
The 2-state controller (ON/OFF controller) switches the output when the setpoint is reached. If the value falls below the setpoint by a certain adjustable tolerance (xsd, switching differential, hysteresis), then the output is switched on again. It therefore only has two switching states. It is used in temperature control applications where the heating or cooling is only switched on or off. A 2-state controller with dynamics can, however, also operate with a P, I, or D component.

Two-State Controller
- Controller output (relay)
- Limit value output (relay) for alarm indication
- Analog output configurable as actual value output, setpoint value output, or logic output 0/10 V for control of solid state relay
- LCD display for process information
- USB interface on front and setup program for simple startup
Control of temperatures, pressures, and other process variables
Multichannel Process Controller
Multichannel Process Controllers are used where there are multiple Temperature Controllers to be used across the process. They can take multiple Process inputs at the same time. Multiple Process variables can be monitored at the same time.
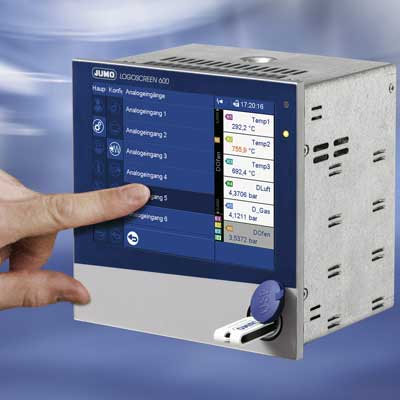

Multichannel Process Controller
- Vibrant TFT touchscreen with intuitive operation
- Precise control of 2 processes
- Easy-to-use program generator control and program entry
- Interfaces: USB host, USB device, Modbus, PROFIBUS DP, PROFINET IO device, and Ethernet
- Process-data recording with tamper-proof data storage
- Individual process-screen display with configurable edit boxes
- Math and logic modules
- Flexible through modular hardware
- Password-protected user management
- Five-digit analog-value display
- Individual user and parameter level
- Control loop and output value monitoring
- Integrated timer (time-switch contacts) as well as service counter and operating hours counter
- Web server for online-visualization via web browser
- Alarm transmission by email
- Protection type IP66
Industrial furnace construction Test chambers and heating cabinets Climatic and simulation chambers Incubators Autoclaves Dryer Sterilizers Heat transfer oil plants Plastics industry Mechanical and plant engineering Test benches Regular food and luxury food Pharmaceutical and chemical industry Use on ships
Temperature Controller
For accurate control of the process temperature without constant operator involvement all industrial thermal process relay upon a controller. The controller gets is inputs from contact temperature sensors like thermocouple, RTD or from a non-contact temperature sensor like an infrared temperature sensor. The controller transmits an electrical signal (current or voltage) to a power switch device which can be a simple relay, a solid state relay or a SCR (Silicone Controlled Rectifier). A temperature controller is an device that is used to control temperature. It does this by first measuring the temperature (process variable), it then compares it to the desired value (set value). The difference between these values is known as the error (Deviation). Temperature controllers use this error to decide how much heating or cooling is required to bring the process temperature back to the desired value. Once this calculation is complete the controller will produce an output signal that effects the change required. This output signal is known as the (manipulated value) and is normally connected to a heater, control valve, fan or some other "final control element" which actually injects or removes heat from the process.
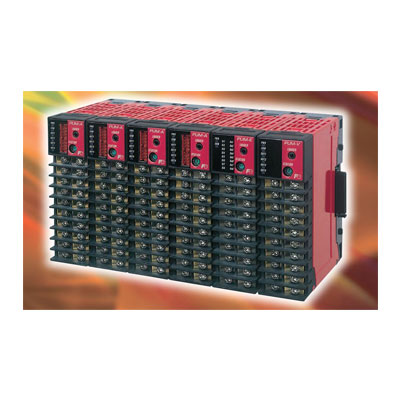

Temperature Controller
- ItŌĆÖs provides proportional with integral and derivative control
- ItŌĆÖs helps the unit automatically compensate for changes in the system
- ItŌĆÖs individually adjusted or "tuned" to a particular system using trial and error
ON-OFF Control. PID Control according to the process. Controlling load by monitoring Temperature. Fuzzy control for any process Plastic Processing Packaging Ovens Water Bath Furnace Heat sealing Extruder Machines Autoclaves for sterilization
Programmable logic Controller (PLC)
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) also known as Industrial Computer is the major component in the industrial automation sector. Due to its robust construction, exceptional functional features like PID controllers, sequential control, timers and counters, ease of programming, reliable controlling capabilities and ease of hardware usage ŌĆō this PLC is more than a special-purpose digital computer in industries as well as in other control-system areas. Different types of PLCs from vast number of manufacturers are available in todayŌĆÖs market. Therefore, in the subsequent paragraphs, let us study about PLCs and their types.
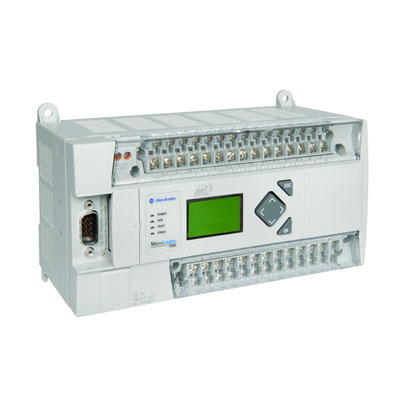

Programmable logic Controller (PLC)
- Cost effective to control complex systems.
- Flexible and can be reapplied to control other systems quickly and easily.
- Computer skills allow more sophisticated control.
- Troubleshooting accessories make programming easier and reduce downtime.
- Reliable components make them work for years before failure.
- Less manpower for design
- Downsizing and standardization
- Improved maintainability
Continuous bottle filling system Batch mixing system stage air conditioning system Traffic control
Distributed Control System (DCS)
Distributed Control System is most popular which is specially designed with redundancy and diagnostic capabilities to improve control reliability and performance. It gives greater flexibility to control distributed discrete field devices and its operating stations In this era of revolution technology, industrial automation system deals with advanced automation control technologies to have better control performance over complex processes..
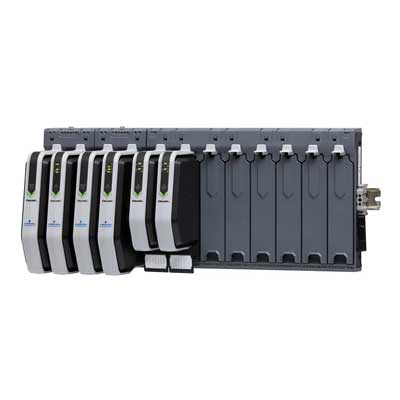

Distributed Control System (DCS)
- Data presentation is in a systematic format enabling easy comparison of various parameters and taking decision by a printer.
- Logging of data is done by a printer thereby eliminating human error.
- It is possible to control through dynamic graphic.
- OperatorŌĆÖs action can be logged, thereby eliminating confusion.
- The alarm system can be regrouped.
- Complex computations, analysis, etc. can be carried out easily.
- Management information can be generated at regular intervals.
- The super-imposed trends helps in the analysis of plant parameters and
- Hardcopy gives the actual dynamic printout at a particular instant.
- The controlling software used is very simple and the application is readily The software changed in one unit has no impact on other units and hence
- the system becomes very flexible. UserŌĆÖs risk in software is minimum.
Chemical plants, Petrochemical (oil) and refineries, Pulp and Paper Mills, Boiler controls and power plant systems, Nuclear power plants, Environmental control systems, Water management systems, Water treatment plants, Sewage treatment plants, Food and food processing, Agrochemical and fertilizer, Metal and mines , Automobile manufacturing, Metallurgical process plants, Pharmaceutical manufacturing, Sugar refining plants, Agriculture Applications
SCADA
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) refers to industrial control systems (ICS) that are employed to control and keep track of equipment or a plant in industries like water and waste control, telecommunications, energy, transport, and oil and gas refining. SCADA is a computer system used to gather and analyze real-time data. This data is processed by the computer and is presented on a regular basis. SCADA also saves and make logs for every event into a log file that is saved on a hard drive or is sent to a printer. SCADA gives warnings by sounding alarms if situations develop into hazardous scenarios.
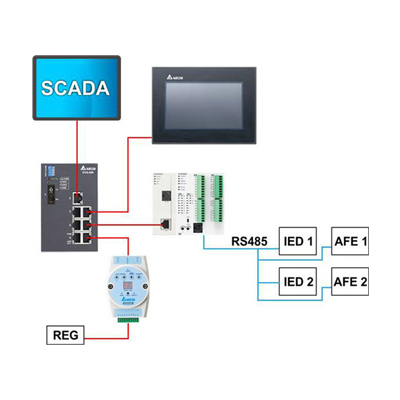
SCADA
- The system provide facility to store large amount of data.
- The data can be displayed in various formats as per user requirements.
- It provides interface to connect thousands of sensors across wide region for various monitoring and controlling operations.
- It is possible to obtain real data simulations with the help of operators.
- Many types of data can be gathered from RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) connected with the master unit.
- With the advanced protocols and application softwares, the data can be monitored from anywhere and not just from local site.
- The redundancy of units are incorporated in the SCADA system in order to have backup in the event of faults or failures. This makes system more robust.
- It is fast in obtaining response.
- It is scalable and flexible in adding additional resources.
- It is used in wide industries and departments including telecommunications, energy, transportation, oil & gas, water, military, meteorological etc.
SCADA systems are used for monitoring a variety of data like flows, currents, voltages, pressures, temperatures, water levels, and etc., in various industries. If the system detects any abnormal conditions from any monitoring data, then the alarms at the central or remote sites will be triggered for alerting the operators through HMI. There are numerous applications of SCADA systems, but a few most frequently used SCADA applications include: Manufacturing Industries Waste Water Treatment and Distribution Plants SCADA in Power System
















